Morphological
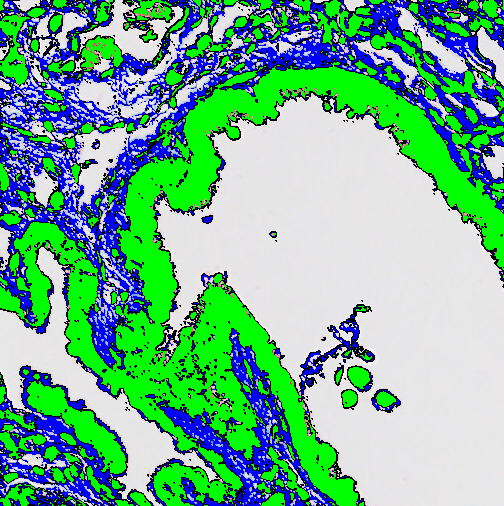
Erode
This step will replace the edge of a label with a chosen label. This is also called erosion.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | Choose a label to erode. |
| With | Choose the label to use for replacing the label chosen above. |
| Pixels | Choose the size of the kernel (convolution matrix) to erode with. The erode uses a circular kernel where the Pixels setting can be seen as the diameter of the circle it erodes with. |
| Apply from image border | Toggles whether or not the image border counts as part of the surrounding label. |
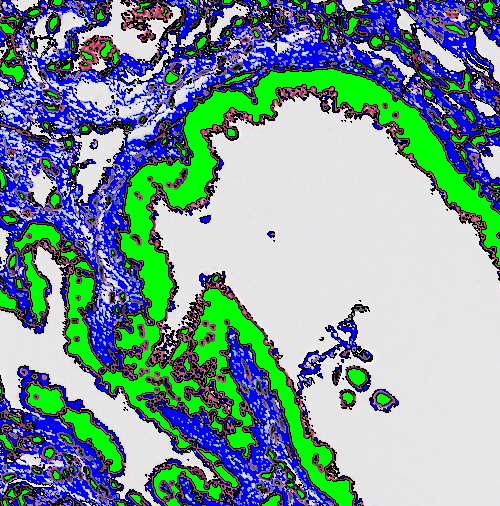
Dilate
This step will dilate the edge of a label with a chosen label. When an edge is dilated a new "layer" is added to the edge.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Object Label | Select a label to dilate. |
| With | Select the label to use for dilating the previously selected label. |
| Pixels | Select the size of the kernel (convolution matrix) to dilate with. The dilate uses a circular kernel where the Pixels setting can be seen as the diameter of the circle it dilates with. |
| Avoid merging objects | If checked, this options sets an exclusion distance which ensures that objects do not merge if their dilation boundaries overlap (only if the overlap is between two or more different objects). |
| Exclude labels | Chose one or more labels that the dilation should not affect. |

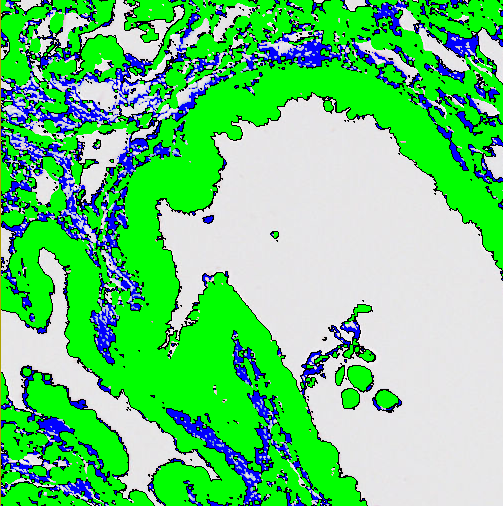
Open
Open corresponds to an erosion followed by a dilation. This will remove small/thin parts of the label objects.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | Choose a label to open. |
| With | Choose the label to use for replacing the label chosen above. |
| Pixels | Choose how many pixels the label should be opened with. |
| Apply from image border | Toggles whether or not the image border counts as part of the surrounding label. |
Close
Close corresponds to a dilation followed by an erosion. This will smooth the edges and fill small holes within the label objects.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | Choose a label to close. |
| With | Choose the label to use for replacing the label chosen above. |
| Pixels | Choose how many pixels the label should be closed with. |
| Exclude labels | Highlight one or more labels that should remain uninfluenced by the close step. |
Skeletonize
This creates a skeleton, which is a line of pixels running along the center of each label object. If the object contains appendices or other irregularities, the skeleton will split to follow each appendix.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | Choose the label to skeletonize. After skeletonization, the skeleton will still have this value. |
| New label | Choose the label to use for replacing the label pixels which are not part of the resulting skeleton. |
| Branch points | Choose the label to use for the pixels placed where the skeleton branches. |
| End points | Choose the label to use for the pixels placed where the skeleton ends. |
| Prune until ... endpoints | Check the check box to use this option. Choose the maximum number of ends to retain in each object skeleton. |
Fill Holes
This step will fill all holes within the chosen label.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Object label | Choose the label whose holes should be filled. |
| Fill label | Choose the label which should fill the holes. |
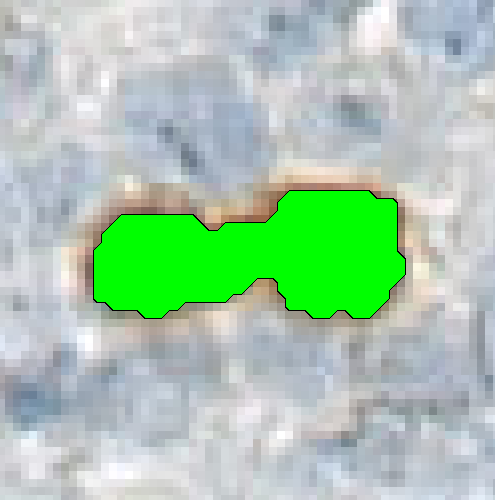
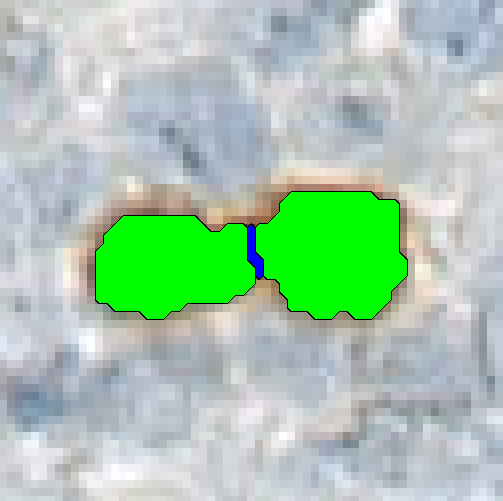
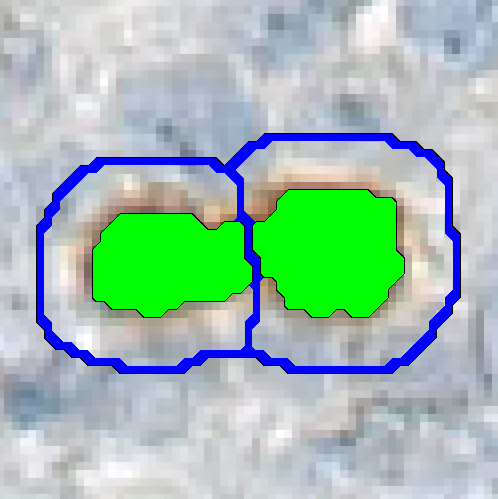
Separate Objects
This step will separate individual objects, that have been merged into one label by a classification. The separation is based on the shape and size of the objects. It is possible to separate the entire image into regions using the objects as templates.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Object label | The label defining the objects to be separated. |
| Separator label | The label which should be used as the separating label. This should be a neutral label, not used anywhere else. |
| Background labels | Define which label(s) that make(s) up the background. |
| Object diameter | The approximate mean diameter of the objects to be separated in the image. This parameter should be in the units used. To measure the diameter and set the unit, use the Measure-tool. |
| Separate object surroundings | If checked the entire image will be separated into regions using the objects in the chosen label as a template. If unchecked the separation is only done inside the chosen object. |
| Surroundings width | If Separate object surroundings is selected this option is available. Define how far out the object boarder can go in units used. This will affect the size of the regions. |
| Assume that objects are elliptic | Assumes that the separated objects are elliptic. If this is not the case and their elliptic score is lower after separation, the objects will stay merged. |
| Object heatmap | Uses a chosen feature from the pre-processing step to assist the separation. The feature should enhance edges (in light colors) and the background (in dark colors). The influence is decided by the span of pixel values, where the range from 0-255 should be default and weighs the heatmap and the distance transform equally. If the span is wider the heatmap will have higher influence than the distance transform and vice versa. |

Separate by Watershed
This step will separate the object-label between seeds that are defined by the seeds-label. The resulting borders between the seeds are labeled with the separator-label. This is done using a watershed algorithm. The watershed algorithm uses a feature image to grow from the lowest pixel values (darkest) and up towards higher pixel values (bright), using the seeds as starting points. Hence the feature image should be constructed such that the pixels for the seed area have low values and pixels at the borders have high values.
Unlike the Separate Objects step, there is no need to specify object size since the algorithm allows unlimited growth within an object, which can follow irregular shapes.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Seeds | The label defining the starting points for the watershed algorithm. |
| Objects | The label defining objects to be distributed between seeds. |
| Separator | The label used to replace the borders occurring from the object separation. |
| Feature | The feature image used by the watershed algorithm. The pixel values at the borders need to be high (bright), while the pixel values at the seeds needs to be low (dark). |
Outline Cells
The Outline cells post processing step will try to outline a given label as if it was a nucleus, by means of interpolation with an already existing membrane label. This step is usually used when the membrane detection has not been good enough. The processing step has four input parameters:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Object center | Defines the nucleus label. |
| Outer limits | Defines the membrane label. |
| Max distance | Defines the maximum distance the outline is allowed to expand (radius from nucleus). |
| Delimiter | Defines the label of the outline. |
Circumscribed Rectangle
Circumscribed Rectangle creates the smallest possible rectangle around a given label, whereas inscribed rectangle creates the largest possible rectangle within a given label.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | Choose label of which to find the circumscribed/inscribed rectangle. |
| Circumscribed | Choose the label assigned to the circumscribed rectangle - choose "Don't use" to ignore. |
| Inscribed | Choose the label assigned to the inscribed rectangle - choose "Don't use" to ignore. |
| Allow rotation | If selected the rectangles are allowed to be rotated, otherwise they are always parallel to the sides of the image. |
Mark Center of Mass
This post process step finds the given labels center of mass, per object, and marks it with another label. The width parameter is the diameter of the circle that marks the center of mass.
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
| Label | The label that will have its center of mass calculated. |
| Mark with | The label that will mark the point in which the located center of mass is. |
| Width | The width of the marked label. |