Tissuealign
The Tissuealign article contain information about aligning images. It provides information regarding import of data, linking images, review/correct the alignments and how to apply a protocol to the images.
If both Tissuealign and Tissuearray are installed, the VirtualDoubleStaining (VDS) module can be used. VDS is a novel and patent protected method for automated, robust and verifiable tumor and stroma separation in Tissue Microarrays (TMAs) and whole tissue sections.
Linking images
After selecting suitable images and importing them into a folder in the database, they can be linked. Linking of the images must be done before automatic alignment can be performed.
To link images, select an image and Alt + click another image in the database to view the images side by side. Any number of images can be selected this way. Once the desired number of images is selected, proceed to correcting the alignment.
Clicking the Auto Link button in the ribbon will open the Automatic Linking dialog, which will enable linking of images based on the names of the files. There are two main methods for defining the pattern which describes the images to be linked, Delimited and Fixed Length.
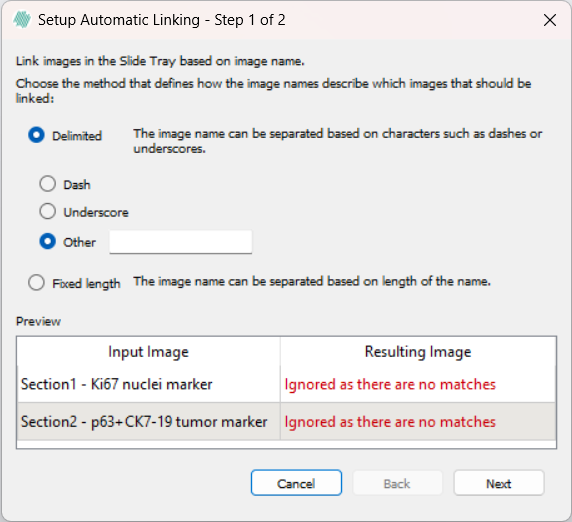
Using the Delimited option, either a dash "-", an underscore "_", or a custom delimiter can be chosen to select which input images will be linked. The custom delimiter is case sensitive and should be a single character. The last appearing delimiting character will be used to select the images. If an image will not be linked using the currently selected pattern, a warning will be displayed reading "Ignored as there are no matches".
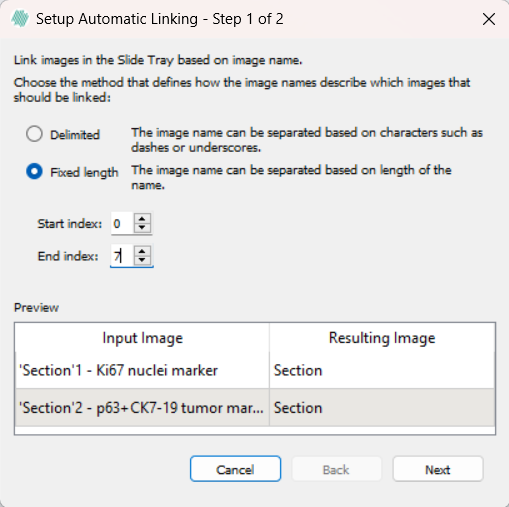
The Fixed Length option has two inputs, start index and end index. Each image where the name is equal between the indexes will be selected for linking. If both indexes exceed the length of the names, the images will be treated as having the same text between the indexes, and will be linked.
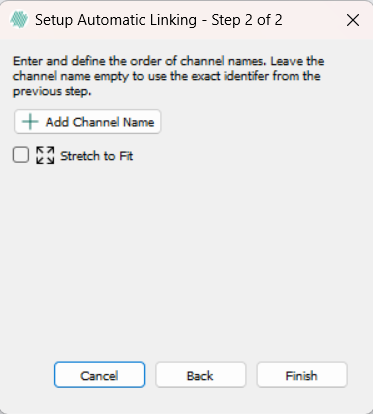
After choosing a method for which images to link there is an option to either keep the name for the channel as created by the method or to rename the channel by clicking the Add Channel Name button. Clicking Finish will promt a save window, where you can select an appropriate place to save the autolinked image.
The image can now be found in the saved location. You can now scroll through the image and attached channels/segmentation masks by pressing the Page Up and Page Down keys.
Review and correct alignment
You should always review each aligned slide to evaluate whether a correction of the alignment is necessary or not. Reviewing can be done by navigating the different images which have been linked and by using the Page Up and Page Down keys. If the review reveals that the first alignment is insufficient and a correction is necessary, you have two options:
| Option | Description |
|---|---|
 | Automatic alignment based on current pin points (Semi-automatic alignment). Selecting this option will align the images based on the placed pin points, and then do a more detailed alignment using the built-in automatic aligner. |
 | If no pins are palced, this button replaces the Automatic alignment based on pin points button. |
 | Apply current pin points to image (Manual alignment). This alignment option will use only the pin points to align the images. |
In both cases it is recommended to place at least 3 pairs of pins on notable locations in the image to reach a good final alignment. When choosing notable locations in the tissue, avoid placing pins in edge regions of the tissue, as there is a risk of this tissue being damaged. When placing a pin in one image, a corresponding pin must be placed in other images of the alignment. If multiple pins are placed in a row in one image, the corresponding pins must be placed in the same order in other images.
When finding notable locations in the tissue slides activating or deactivating image viewing lock might be an advantage.
This can be done ensuring the  button is clicked (it is enabled by default). The viewing of the linked can be reset to the default view by clicking the
button is clicked (it is enabled by default). The viewing of the linked can be reset to the default view by clicking the  button.
button.
Tissuealign also provides 3 helpful tools to ease the correction process:
| Tool | Description |
|---|---|
| Ctrl+Z | Undoes only the last pin point added to one of the images. This tool helps you as you can undo a misplaced pin point. You can undo multiple pin points one by one by clicking the shortcut multiple times. |
 | Deletes all pin points added to all current displayed images. Only use this tool if you are absolutely sure you want to delete all pin points. Pressing Ctrl + Z will undo the deletion of all pins and restore them. |
 | Use this tool if you apply an unsuccessful alignment and want to undo it. E.g. if you apply an manual alignment but the previous automatic alignment was better, you can go back to the automatic alignment result by undoing the manual alignment. |
The alignment should be reviewed again to evaluate whether another correction of the alignment is necessary or not. If the alignment is insufficient again, you can try to increase the number of pin points.
Alignment using ROIs
Alignment can also be done using ROIs. This is especially useful if dealing with damaged tissue that requires exclusion from the alignment process.
To align two or more images using ROIs, simply draw any type of ROI around the relevant tissue(s) in each image and click Auto align. When ROIs are present, aligment will only be performed based on pixels that are inside ROIs.
For aligning regions within a single image, multiple versions of the image need to exist in the database. This can be achieved by duplicating the image with a different name or saving it in a different location in the database. Alternatively, following the Tissuearray workflow to dearray tissues in the image will also allow for the creation of multiple images in the database. Once multiple images exist in the database, the above workflow can be employed to align them.
Processing of alignment
Once the alignment is sufficient, ensure that the alignment is saved. An APP or a series of APPs can now be run on the aligned images and the output of the APPs will be visible on all parts of the alignened images which can be viewed by pressing the Page Up and Page Down keys.
Most default APPs will only run on one of the aligned images. Changing which image the APP should run on can be done in the APP Author in the Classification tab.