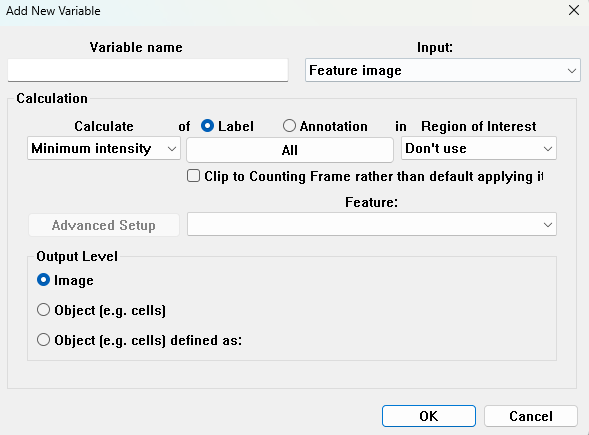
Feature Image
If Feature Image is selected as input, the desired feature should be selected from the Feature list.
- Calculate - Select from several statistic calculations to be performed on the selected input.
- Label - Specify one or all of the labels on which the calculation should be performed.
- ROI - Specify one or all ROIs to limit the object. Only labeled pixels inside the ROI(s) are used in the calculation. It is also possible to choose not to use any ROIs to limit the objects.
- Variable name - Specify a name for the variable. If the name is already used, the variable is not added to the list.
- Limit calculations to the inside of the counting frame - Only available when a counting frame is added in the preproccesing steps.
Calculate
The following calculations can be performed on the feature image:
Minimum intensity
The minimum intensity of the given label or annotation for the specified feature is saved as the output variable.
Maximum intensity
The maximum intensity of the given label or annotation for the specified feature is saved as the output variable.
Mean intensity
The mean intensity of the given label or annotation for the specified feature is saved as the output variable.
Standard deviation
The standard deviation of the intensity for the given label or annotation for the specified feature is saved as the output variable.
Median
The intensity of each label/annotation is calculated in the specified frame and band. The median of the calculated intensities is saved as the variable.
Modus
The intensity of each label/annotation is calculated in the specified frame and band. The modus of the calculated intensities is saved as the variable. The modus is the most frequently occurring pixel value (if this includes several values or non-repeating values the lowest value will be saved).
Entropy
The entropy of the given label or annotation and specified band is saved as the output variable. Entropy is a measure of the randomness of the chosen chosen object, where a greater value indicates grater randomness. Entropy is estimated as a probability distribution:
where is the entropy, is the number of bins, and is the probability of a data point falling into the -th bin.
The entropy is based on a number of bins (nBins) used in the histogram calculation. Choosing many bins will allow for more precision, but will be more sensitive to noise, while fewer bins will be more resilient to noise, but might lose information.
Texture measures
The texture measurements of a given label or annotation are calculated based on the chosen band. There are six different texture measures available.
- Texture Inertia: The texture inertia is the inertia of the power spectrum. Inertia of an image can be described as the force needed to accelerate the image to a rotation around the center of the image. This means that texture inertia mainly quantifies how high the frequencies in the image are.
- Texture Entropy: The texture entropy is the entropy of the power spectrum and describes how much randomness there is present in an image.
- Texture Minor Axis: The texture minor axis is the length of the minor axis of the power spectrum, modeled as a 2-dimensional Gaussian distribution. The texture minor axis will be proportional to the frequency orthogonal to the highest frequency in the image in any direction.
- Texture Major Axis: The texture major axis is the length of the major axis of the power spectrum, modeled as a 2-dimensional Gaussian distribution. The texture major axis will be proportional to the highest frequency in the image in any direction.
- Texture Anisotropy: The texture anisotropy is the relation between the minor and the major axis of the power spectrum, modeled as a 2-dimensional Gaussian distribution. The texture anisotropy is proportional to how much directional information there is present in the image.
- Texture Major direction: This texture measurement specifies the direction of the most prominent texture. The direction is given in relation to the horizontal axis and will be between 0 and 180.
Pixel Values
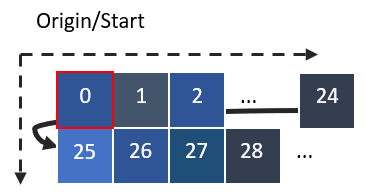
The pixel value feature outputs the pixel values in a given label(s) of the given band in the current FOV (Tile analysis size). The output can create massive amount of data. The total number of included pixels in whole slides is therefore limited to the number of pixels in a single FOV.
The order of the pixel data when displaying Origial Data will be as the position in the origial FOV. The first point will be the value in the top left hand corner and following values are from pixels moving left to right for each row of pixels.